ENG360 - iOA
(Industrial Operation Automation)
There’s no slowing technology down, and you need a CRM that can keep up. Since Sugar is engineered in AWS, we’re able to deliver more innovative and cost-effective CX initiatives for every Sugar customer. Simplify your CRM world without slow or costly implementation, increase adoption by removing busy work from employees, and see your revenue grow.
Key Benefits


SBAS (Smart Building Assessment System)
The quality assessment systems platform drives improved benchmark the quality of all-important internal finishing of a building, as well as the external features such as the building facade and its amenities and supporting infrastructure, through the use of bespoke digital form creation, and digital approval workflow.
Key Benefits
SCSS
(Smart Corporate Secretarialship Services)
SCSS is the Next Generation's Digital Transformation Solution for Corporate Secretarial services
Key Benefits


IMS (Invoice Management Systems)
Invoice management software plays a crucial role in helping companies automate and optimize tasks related to invoice processing. When invoices are received, they typically undergo an approval workflow and are matched with sales or purchase orders and payment records to ensure accuracy.
These software solutions streamline the entire process by using technologies such as OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to scan invoices, extract key data, and automatically populate system fields. Some platforms also support electronic payments and mobile access, enabling users to approve invoices remotely.
Key Benefits
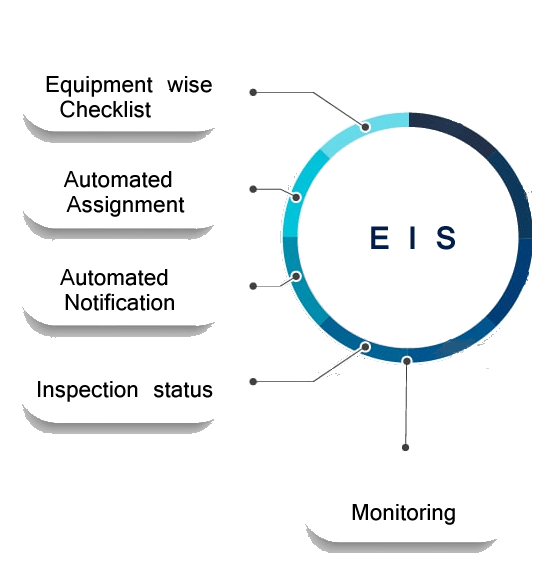
EIS (Equipment Inspection Systems)
EIS is designed to streamline and standardize the process of conducting routine and periodic inspections and audits on equipment and their components. By ensuring compliance with construction and engineering specifications, EIS helps organizations maintain high standards of quality, safety, and operational efficiency.
Application covers the organization’s hierarchy & documentation section is been completely automized, user end trainings & handling the equipment inspections, preventive measures & equipment maintenance in detail.
Key Benefits
Alegre Ventures Pte. Ltd.
(Your Trusted DX Partner)
Digital transformation has the potential to drive significant improvements in efficiency and productivity, and it is an important consideration for any organization looking to stay competitive in today's digital world.
Key Benefits
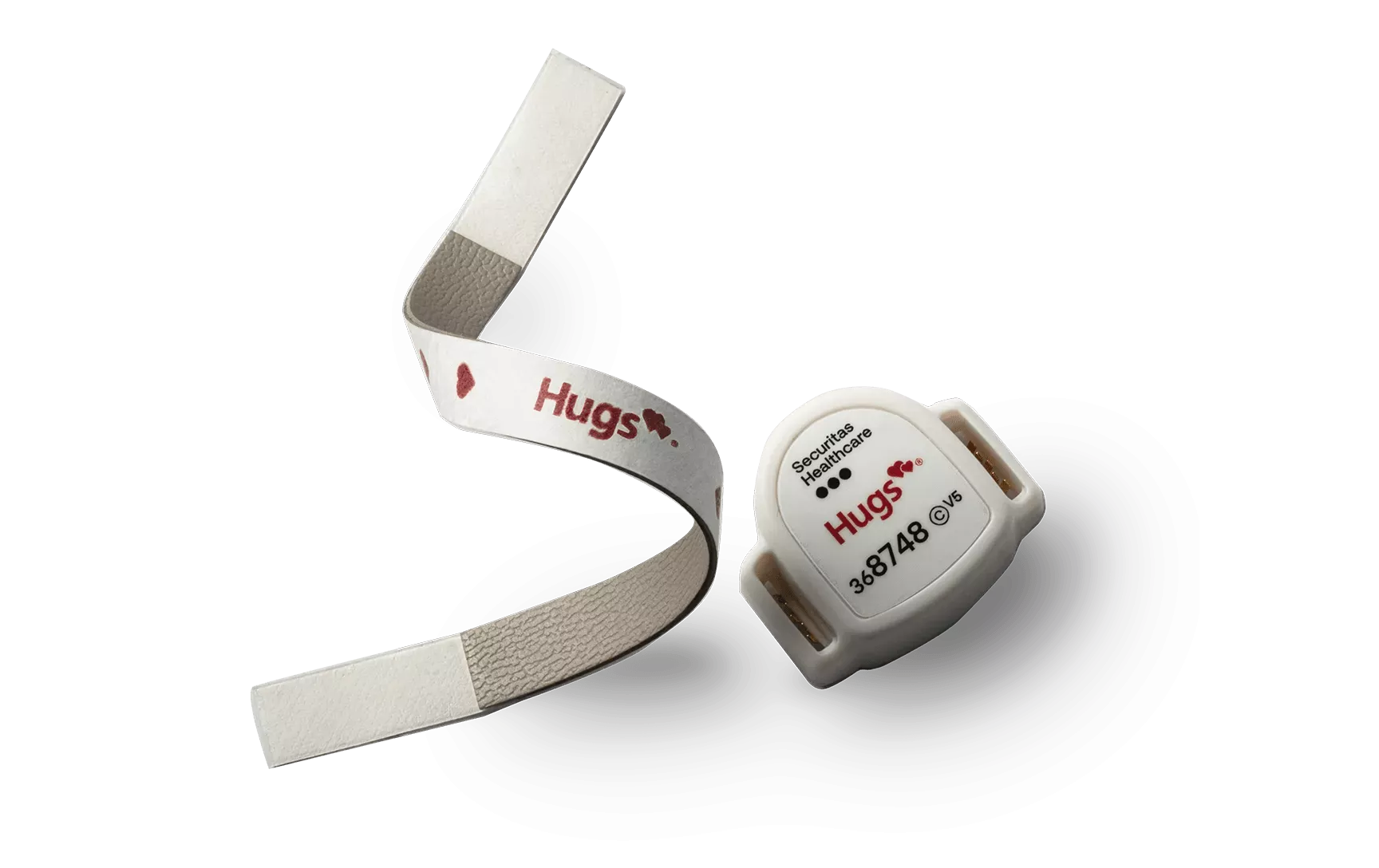


Securitas Healthcare (Hospital-Wide Protection)
The Hugs® Infant Protection System by Securitas Healthcare is a leading security solution designed to safeguard newborns, pediatric, and NICU patients in hospitals through advanced, multi-layered protection. Trusted by over 1,780 hospitals worldwide, it offers tamper-proof infant tags, real-time alerts, automated mother-baby matching via the Kisses® tag, and seamless point-of-care integration for clinical staff. Its lightweight, hypoallergenic design ensures infant comfort, while automated workflows and scalable deployment make it ideal for facilities of any size. With built-in alarm systems and robust support services, Hugs provides unmatched safety, efficiency, and peace of mind for caregivers and families.
Streamline workflows, receive real-time alerts, and access comprehensive support with Hugs. Simplifying tag management, enhancing bedside care, and ensuring infant security hospital-wide.
Key Benefits
SugarCRM
(Technology & Software)
Integrating ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) with CRM (Customer Relationship Management) provides a unified, real-time data platform that breaks down silos between customer-facing sales and support teams and back-office finance, inventory, and operations. This synergy enables smoother workflows—from quote generation in CRM directly into ERP order processing—while empowering organizations to deliver personalized customer experiences, make data-driven decisions, and scale operations more effectively. SugarCRM enhances this integration further with AI- and ML-powered revenue intelligence tools, such as predictive alerts, churn detection, and guided selling playbooks that leverage the merged customer and operational data for deeper insights and proactive growth.
Key Benefits


Vue.ai’s
(Build Your Own Financial Automation Ecosystem )
Vue.ai’s AI in Finance platform enables financial institutions to automate core processes like onboarding, invoice processing, credit scoring, and fraud detection—all with rapid deployment in under 30 days. With low-code workflows, AI-driven insights, and a unified data hub, it simplifies complex operations and reduces implementation time and cost.
Built with a composable, modular architecture, the platform integrates seamlessly with existing systems, allowing teams to scale and adapt quickly. Real-time analytics, predictive modeling, and expert co-managed rollout ensure smarter decision-making, enhanced compliance, and faster ROI.
Key Benefits

Myttem
(Supply Chain Management)
Myttem by Artiselite is a cloud‑native, modular ERP and Supply Chain Management platform tailored for businesses undergoing digital transformation. Designed with built-in industry best practices, it delivers real-time operational visibility via bar- and QR‑code scanning, streamlined multi-level approvals, AI-driven demand forecasting and procurement planning, and automated workflows. It supports seamless integration with modules like Sales & CRM, Inventory & Warehouse, Purchasing, Manufacturing, Logistics, Accounting, HR, and third-party systems—enabling scalable, agile growth without per‑user charges and with customization support included.
Key Benefits
CloudVerse.AI
(provides an AI-enabled FinOps Platform)
CloudVerse AI is one of the leading multicloud FinOps platforms; built by cloud SMEs, cloud engineers, and data scientists
CloudVerse AI currently delivers a unified cloud management platform that optimizes costs, improves governance & enhancessecurity, and across multiple cloud providers.
Key Benefits

White Blue
(With expertise spanning Cloud, Data, AI, and IoT)
we craft consulting framework (using WhiteBlue’s C3 framework), solutions and deployment model to align with customer’s needs in order to maximize value in a shorter period.
Our way of increasing productivity to Customers is to equip our strong competence team with cutting edge accelerators.
Key Benefits
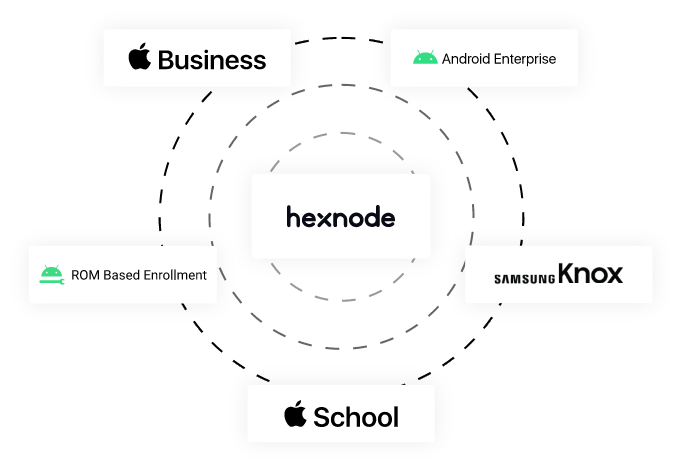
UEM Solution by
Hexnode
Hexnode UEM (Unified Endpoint Management) for Education is a comprehensive cloud-based solution designed to streamline the deployment, management, and security of digital learning devices across schools and academic institutions. With full support for platforms like iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS, Hexnode empowers IT administrators to centrally manage devices used by students and educators. It enables zero-touch deployments, kiosk lockdowns, secure app distribution, network and security configurations, real-time location tracking, compliance monitoring, and much more. Integrated with tools like Apple School Manager, Google Workspace, and Azure AD, Hexnode ensures a seamless and secure e-learning experience while maintaining operational efficiency, data safety, and classroom focus.
Key Benefits
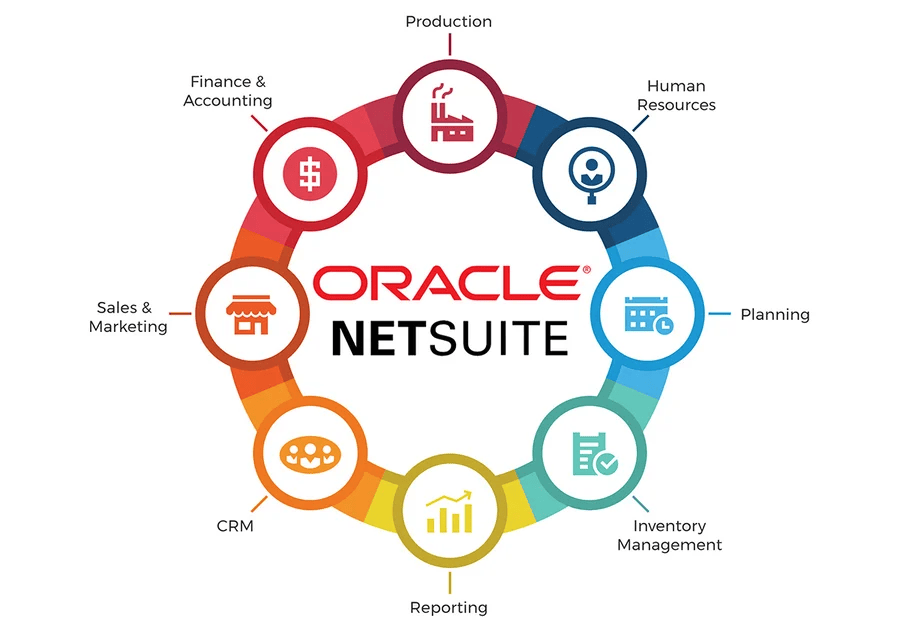
Oracle NetSuite ERP
(AI-powered, cloud business management solution)
Oracle NetSuite ERP is a fully integrated, cloud-native business management platform that brings financials, CRM, inventory, order management, HR, supply chain, and e-commerce together into a single system. Designed from the ground up for the cloud, it delivers real-time visibility across the enterprise via centralized data and role-based dashboards. With modular architecture, built-in automation, extensive customization options, and AI-assisted features embedded at no extra charge, NetSuite empowers organizations of all sizes to streamline operations, scale seamlessly, and drive data-driven decision‑making.
Key Benefits

Payce
(Global Payroll Simplified)
Ramco Payce is a next-generation, platform-based payroll solution designed for medium to large organizations (typically with 1,000+ employees), offering global payroll coverage across 150+ countries. Built on technologies like serverless in-memory computing, AI, and machine learning, Payce enables ultra-fast payroll processing, error-free compliance, and deep automation. Its drag-and-drop rule builder eliminates the need for coding, while guided implementation tools and built-in integrations with leading HCM and ERP platforms help firms onboard swiftly and manage payroll without technical intervention. Suitable for both self-managed deployment and managed payroll services, Payce delivers reliable scalability with real-time analytics, employee self-service portals, and enterprise-grade security.
Key Benefits
Vue.ai(AI-Powered Platform for Retail)
Vue.ai delivers a comprehensive, enterprise-grade AI platform tailored for eCommerce and retail brands. The suite automates product catalog intelligence with computer vision, enables visual search, and powers a dynamic personalization engine that curates product recommendations—such as “complete-the-look” outfits—across webpages, emails, and cart pages in real time. Retailers using Vue.ai have seen tangible results like a 1.5× increase in average order value and over 500% uplift in revenue per user thanks to targeted, intent-aware personalization that adapts to each shopper’s behavior and session-driven intent.
Vue.ai also transforms creative production by generating on-model imagery using its proprietary VueModel tool—enabling brands to showcase inventory on diverse model types without costly photoshoots. The platform enhances catalog accuracy, automates image tagging across thousands of attributes, and enriches product metadata, helping retailers enable faster go-to-market, manage large inventories, and deliver elevated shopper experiences at scale
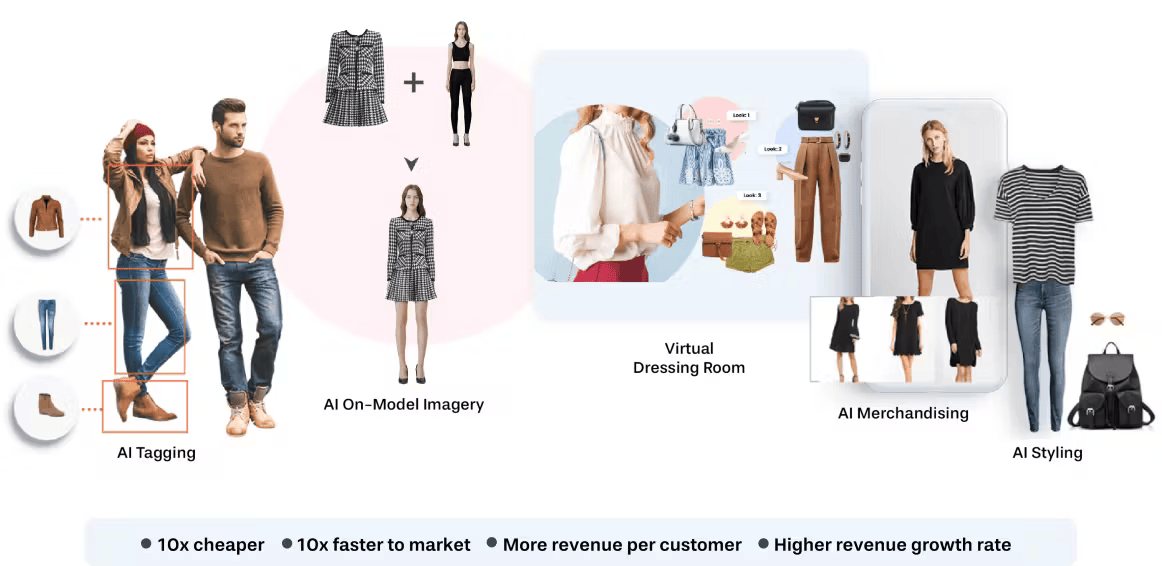
KEY BENEFITS
Energy Vanguard(Energy Management)
Energy Vanguard SG delivers a turnkey energy‑management ecosystem that merges smart hardware, cloud-based analytics, and 24/7 virtual expertise to make buildings smarter, more efficient, and highly cost‑effective. Their flagship system—built around the Eniscope platform (with Air‑suite IoT sensors and CUES for cooling)—provides real‑time, asset‑level visibility, advanced environmental monitoring, alarms, and analytics. Backed by continuous support from their Virtual Energy Manager service, the solution helps businesses across sectors like retail, hospitality, food service, and multi‑site commercial operations simplify energy control, sustain reductions, and fund further upgrades through savings.
Attaining high energy savings and sustaining them needs a combined approach - hardware, software and service working in harmony.
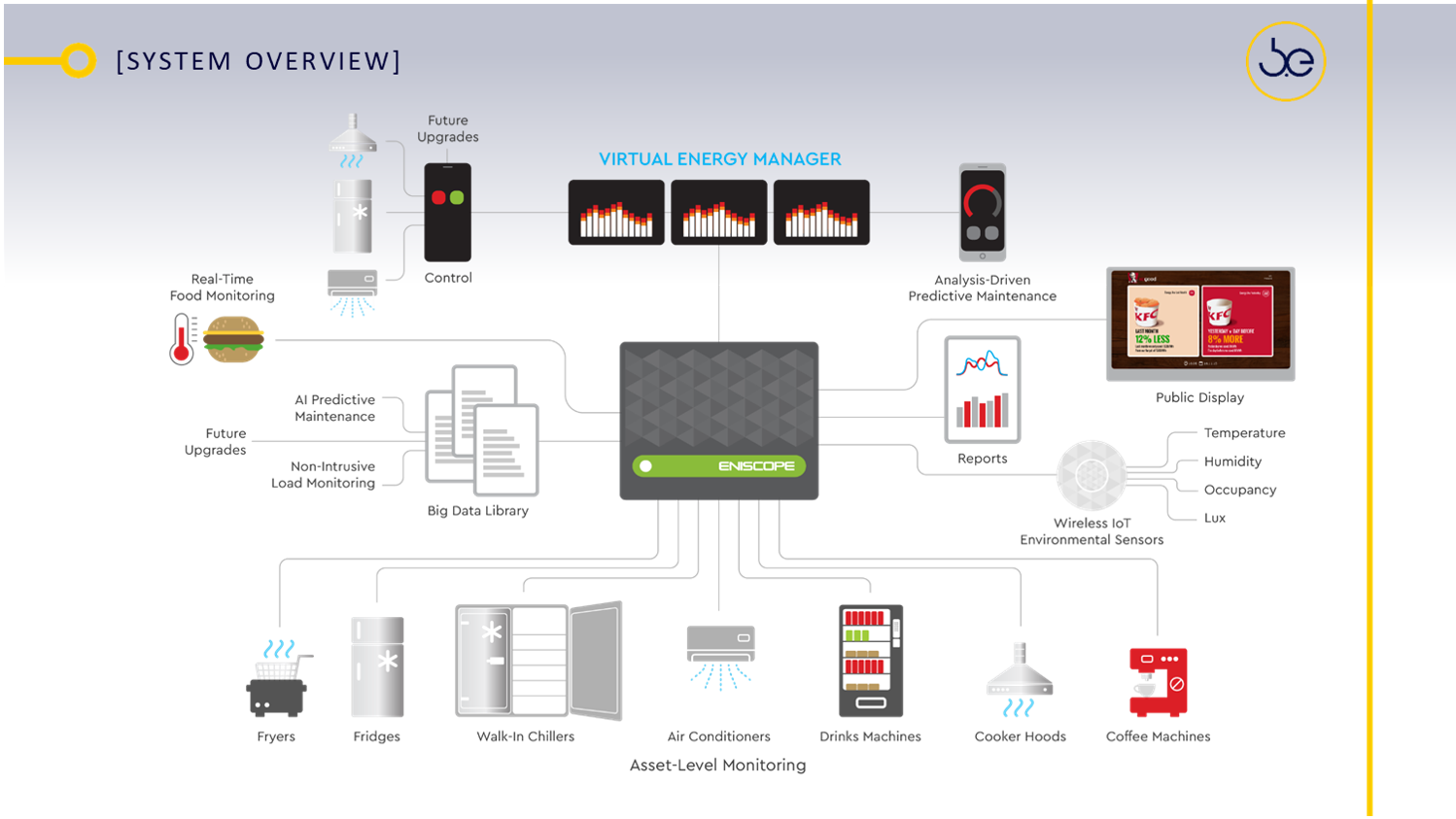
KEY BENEFITS
Vue.ai(AI-Powered Platform for Insurance)
Vue.ai offers a unified, industry‑specific AI orchestration platform designed to automate and optimize the entire insurance value chain for insurers (general, life, health, P&C) and financial services companies.
Full-process automation: From lead scoring and marketing campaigns to underwriting, policy onboarding, servicing, claims processing, and claims disbursement—all handled from a single platform
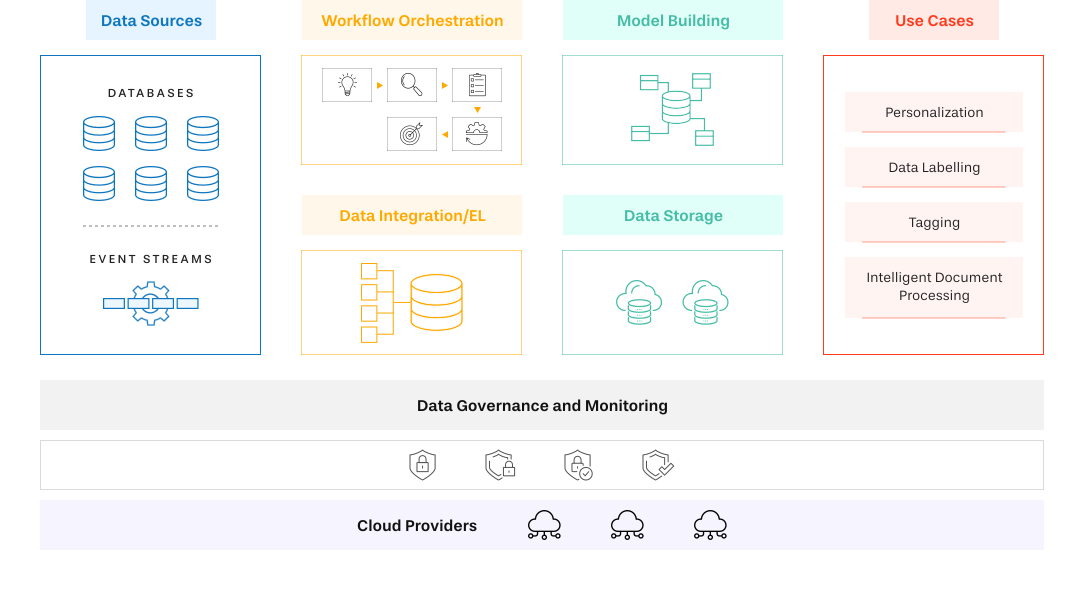
KEY BENEFITS